ISSUE 33:
What is the best tool for measuring bodyfat?
Welcome to the 33rd issue of the ABS newsletter! Today I want to discuss the various bodyfat measurement tools and their relative accuracy and key takeaways when collecting this data. First, we must cite, define and analyze the many methods that exist and are typically used to collect these anthropometric figures. So what are the main methods?
Hydrostatic-Weighing:
2-compartment model.
Uses water displacement to measure body volume.
Uses a conversion equation (Siri equation).
Affected by many variables (hydration, ethnicity, etc).
Individual Error rate of 5-6%
Bod Pod:
2-compartment model.
Uses air displacement to measure body volume.
More variables than hydrostatic-weighing.
Poor at tracking over time.
5-15% individual error rate.
Skin-fold Calipers:
2-compartment model.
Dependent on proficiency of the coach.
Recommended to have the same coach measure.
3.5-5% measurement error.
Compounding error (equation is based on hydrostatic weighing individual error rate 6%).
Individual variability due to unique bodyfat partitioning.
Specific skinfold measurements may provide more useful data.
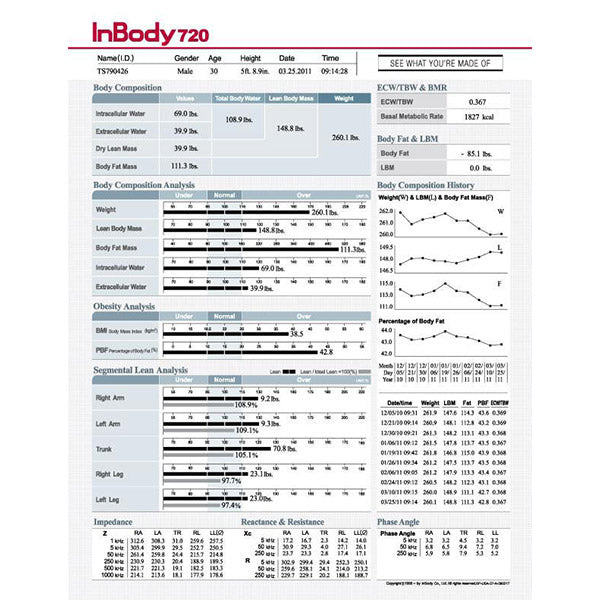
InBody/BIA:
2-compartment model
Most accurate under ideal conditions (isocaloric, fasted, low stress, untrained, normal hydration).
Can be skewed by body water fluctuations and location of adiposity (menstrual cycle).
Electric current will follow the path of least resistance.
Individual error may be as high as 8%.
Error is compounded because estimates are based upon metrics determined by other methods (typically hydrostatic weighing (individual error rate of 6%).
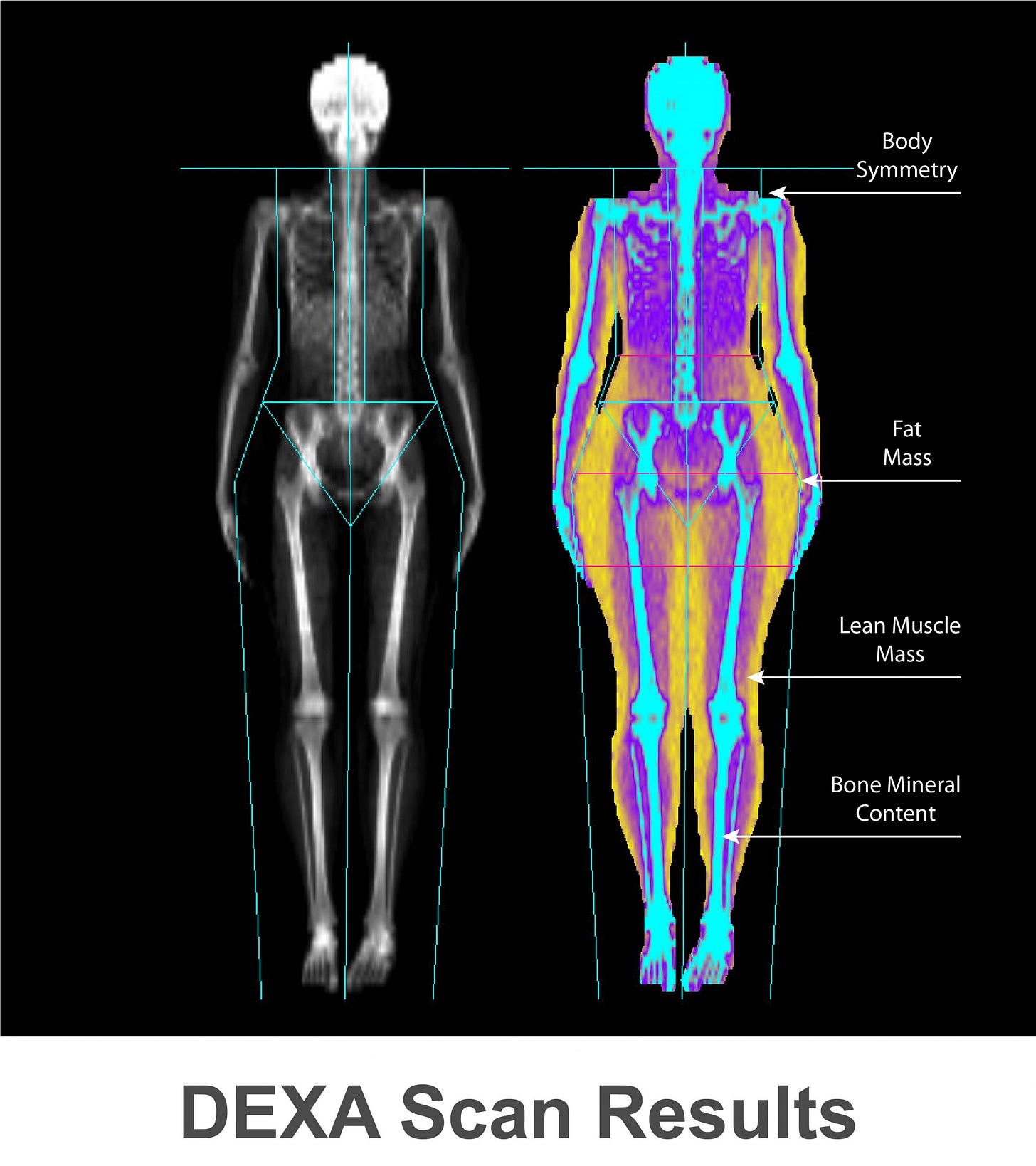
Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA):
3-compartment model.
Estimates fat, bone mineral, and non-bone fat free mass.
Recommended to use the same machine with the same software configurations.
Type of beam (fan vs pencil) can add error.
Hydration status affects estimates.
Can be precise for group averages (1-2% error).
Individual error is around 4-10%.
Perhaps most useful under ideal conditions 1-2x per year.
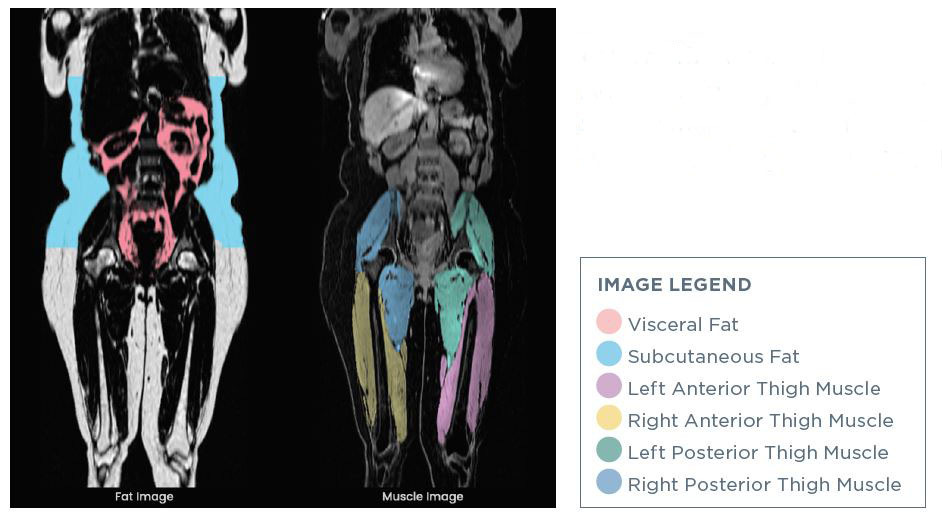
MRI:
High contrast between water and fat
Ideal modality to analyze muscle vs fat tissue without using ionizing radiation
High cost and limited access to an MRI machine
4-Compartment Model
Gold Standard.
Solves for fat mass (using DEXA), total body water (using deuterium dilution), and body volume (using air-displacement plethysmography or underwater weighing).
Reference method by which all other methods are compared to (not practical to implement except in research settings).
The outline of our conversation:
1. General intro.
2. Overview
3. Pros and Cons of each method
4. My top picks
5. My final thoughts and motivation sendoff!
I greatly appreciate your viewership; catch you all in the comments. Stay tuned for the 34th issue next week!